The Automated Natural Language Processing (NLP) Analysis is one of the core features of Error Analyzer. It functions as a systematic scanner that enriches your texts with structured grammatical and semantic information. Unlike the interactive AI Chat, which responds to your questions in real time, the NLP Analysis runs automatically and generates a detailed linguistic blueprint for each sentence. This blueprint forms the foundation for many of the application’s other features, supporting both micro-level analysis and corpus-wide exploration.
It is important to note that NLP analysis, while powerful, is not infallible. Automated systems may misidentify words, misclassify structures, or overlook contextual nuances. For this reason, the output should be treated as a computational aid rather than unquestioned evidence. Researchers are strongly advised to cross-check the system’s output against their own linguistic judgment before drawing conclusions or applying tags.
The Blueprint Viewer: Sentence-Level Insights #
At the level of individual text pairs, the NLP Analysis provides fine-grained linguistic data that can be explored directly alongside your texts.
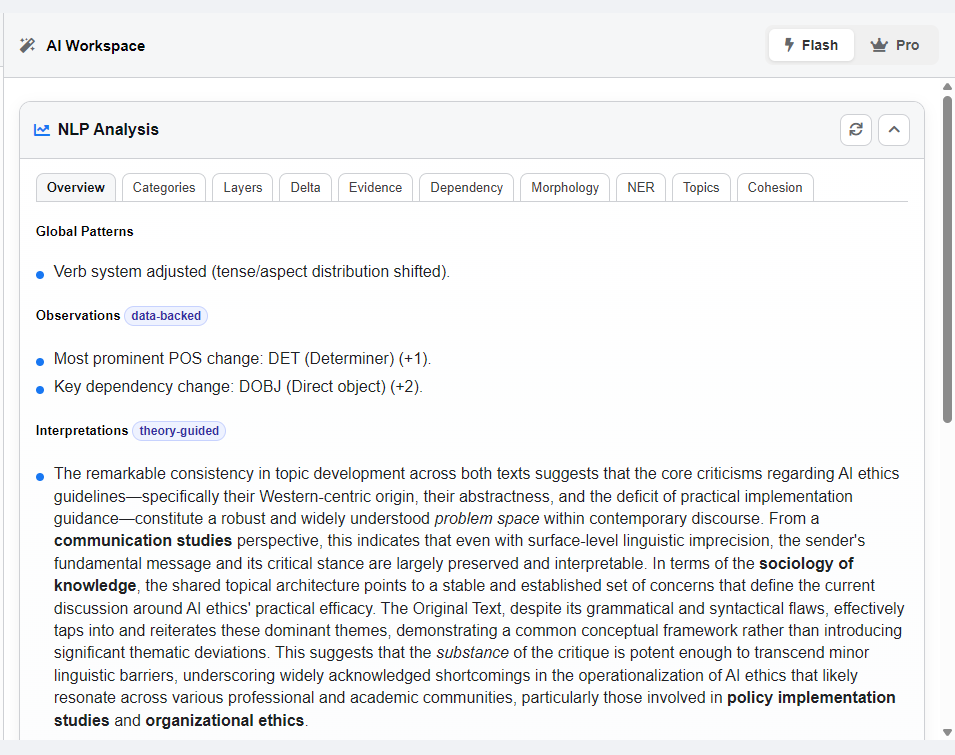
Key capabilities include:
- Revealing grammatical structure:
- Part-of-Speech Tagging: Every word and punctuation mark is identified with its grammatical role (e.g., Noun, Verb, Adjective, Adverb).
- Dependency Parsing: Grammatical relationships between words are mapped, making visible the structural framework of the sentence (e.g., subject–verb, verb–object).
- Named Entity Recognition: Proper nouns are automatically identified and classified into categories such as Person, Place, or Organization.
- Visual exploration: This information is presented directly on the text through color-coding and interactive diagrams. Rather than reading technical notation, you can see sentence structures at a glance, identify relationships, and examine the role of specific words.
- Supporting annotation: The NLP blueprint provides objective linguistic detail that informs your own higher-level tagging. For instance, if the system identifies a verb as being in the past tense, you can use that information to support your own tagging decisions.
This view ensures that every manual annotation is accompanied by a consistent layer of machine-generated evidence, while still leaving final interpretive responsibility with the researcher.
The Blueprint Summary: Corpus-Level Patterns #
When expanded to the entire project, the NLP Analysis moves from sentence-level detail to aggregated summaries, offering a quantitative perspective on your corpus.
Key capabilities include:
- Quantitative corpus linguistics: Frequency counts and distributions of linguistic features are automatically generated. For example, you may see the overall ratio of nouns to verbs across your dataset or the most common grammatical dependencies.
- Identifying high-level patterns: The analysis highlights trends such as the distribution of verb moods (indicative, imperative, subjunctive) or the density of named entities in different sections of the corpus.
- Data for external analysis: The compiled results can be exported for use in statistical tools such as R, Python, or SPSS, enabling you to integrate qualitative annotation with quantitative evidence in your research.
From Blueprint to Interpretation #
By providing both detailed sentence-level information and aggregate corpus-level statistics, the Automated NLP Analysis bridges qualitative and quantitative approaches. It equips researchers with a computational foundation for their annotations, while also offering broad descriptive patterns that can inform theoretical interpretation, pedagogical feedback, or further statistical modeling. At every stage, however, the human researcher remains the final arbiter of accuracy and meaning.